Exploring CAR T-Cell therapy as a treatment for Cancer
Cancer occurs when cells in the body begin to grow in an uncontrolled way. Cells divide and grow when they shouldn’t.
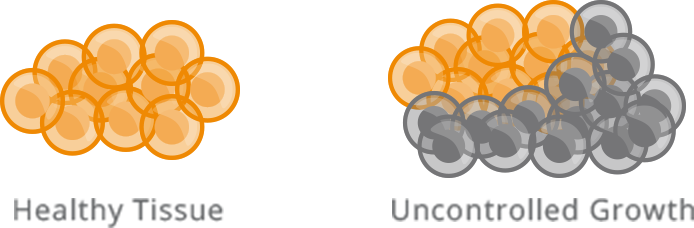
The diseased cells can grow in clumps forming a solid tumor or spread throughout the body known as a blood tumor
CAR T-cell therapy is designed to treat cancer by targeting and eliminating the diseased cancer cells.
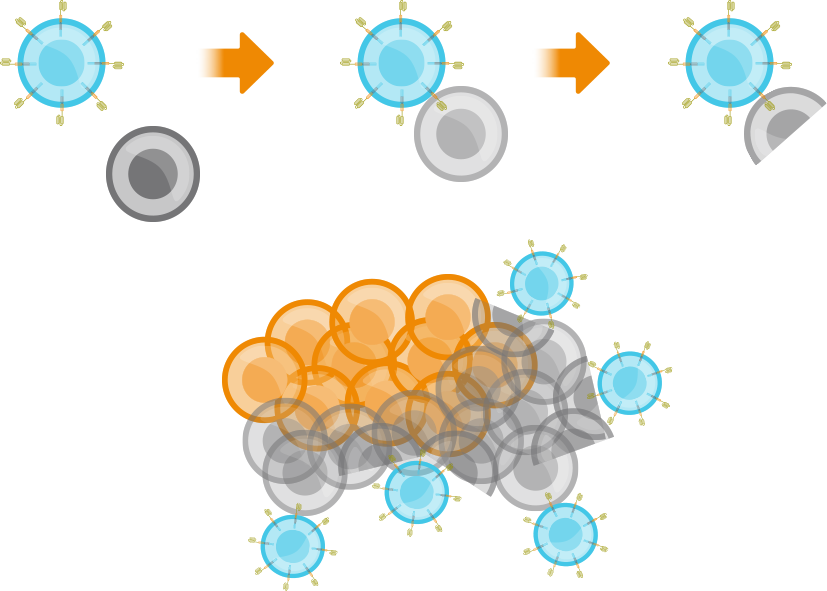
Fate’s investigational CAR- T-cell therapy is designed to explore a more accessible treatment option with the potential for fewer side effects compared to traditional treatments.
Our Indications
Solid Tumors
Multiple Myeloma (MM)
Lymphoma
Solid tumors can occur in various areas of the body including organs, muscles, and bones. Cancer causing tumors, known as malignant tumors, can spread to other areas of the body. Common types include breast, ovarian, lung, and colorectal cancer. Symptoms depend on the tumor location but can include pain, lump(s), changes in body function, and weight loss.
Organs
Solid tumors can occur in various areas of the body including organs
Muscle
Solid tumors can occur in various areas of the body including muscles

Bones
Solid tumors can occur in various areas of the body including bones

Multiple Myeloma is diagnosed when a patient’s plasma cells grow uncontrolled. Plasma cells are a type of blood cell found in bone marrow that normally help fight infections by making antibodies. When there are too many plasma cells, they crowd out healthy blood cells and make abnormal proteins that impact bones, kidneys, and the immune system. Symptoms include bone pain, fatigue, and frequent infections.
Bone
Too many plasma cells can make abnormal proteins that impact the bones

Kidneys
Too many plasma cells can make abnormal proteins that impact the kidneys
Immune System
Too many plasma cells can make abnormal proteins that impact the immune system

Lymphoma begins when white blood cells called lymphocytes grow uncontrolled. These cells play a key role in the immune system to help fight infections and get rid of waste. When there are too many, they build up in areas of the body including the lymph nodes, spleen, or bone marrow. Symptoms include fatigue, weight loss, or fevers.
Lymph Nodes
Uncontrolled lymphocytes can build up in areas such as the lymph nodes

Spleen
Uncontrolled lymphocytes can build up in areas such as the spleen

Bone Marrow
Uncontrolled lymphocytes can build up in areas such as the bone marrow